

There is the possibility for the customer to integrate backwards.The customer knows about the production costs of the product.The product is not of strategical importance for the customer,.Customers could produce the product themselves,.Customers have low margins and are price-sensitive,.Switching to an alternative product is relatively simple and is not related to high costs,.The product is undifferentiated and can be replaces by substitutes,.The supplying industry operates with high fixed costs,.The supplying industry comprises a large number of small operators.They buy large volumes / there is a concentration of buyers,.
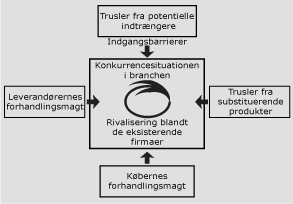
Similarly, the bargaining power of customers determines how much pressure customers can impose on margins and volumes.Ĭustomers bargaining power is likely to be high when The dependence powerful suppliers can potentially reduce strategic options for the organization. In such situations, the buying industry often faces a high pressure on margins from their suppliers. The buying industry has low barriers to entry.reluctance to accept new releases of products), The buying industry hinders the supplying industry in their development (e.g.Forward integration provides economies of scale for the supplier,.The buying industry has a higher profitability than the supplying industry,.There is the possibility that suppliers integrate forwards in order to obtain higher prices and margins.The switching costs from one supplier to another are high,.The suppliers’ customers are fragmented, so their bargaining power is low,.There are no substitutes for the particular input,.The market is dominated by a few large suppliers rather than a fragmented source of supply,.Supplier bargaining power is likely to be high when: The term ‘suppliers’ comprises all input sources that are needed in order to provide goods or services. Market structures, number of players, market size and growth rates Supply and demand theory, customer behavior, price elasticity Supply and demand theory, cost and production theory, price elasticity They take into account supply and demand, complementary products and substitutes, the relationship between volume of production and cost of production, and market structures like monopoly, oligopoly or perfect competition: Porters Five Forces These five forces are based on microeconomics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
